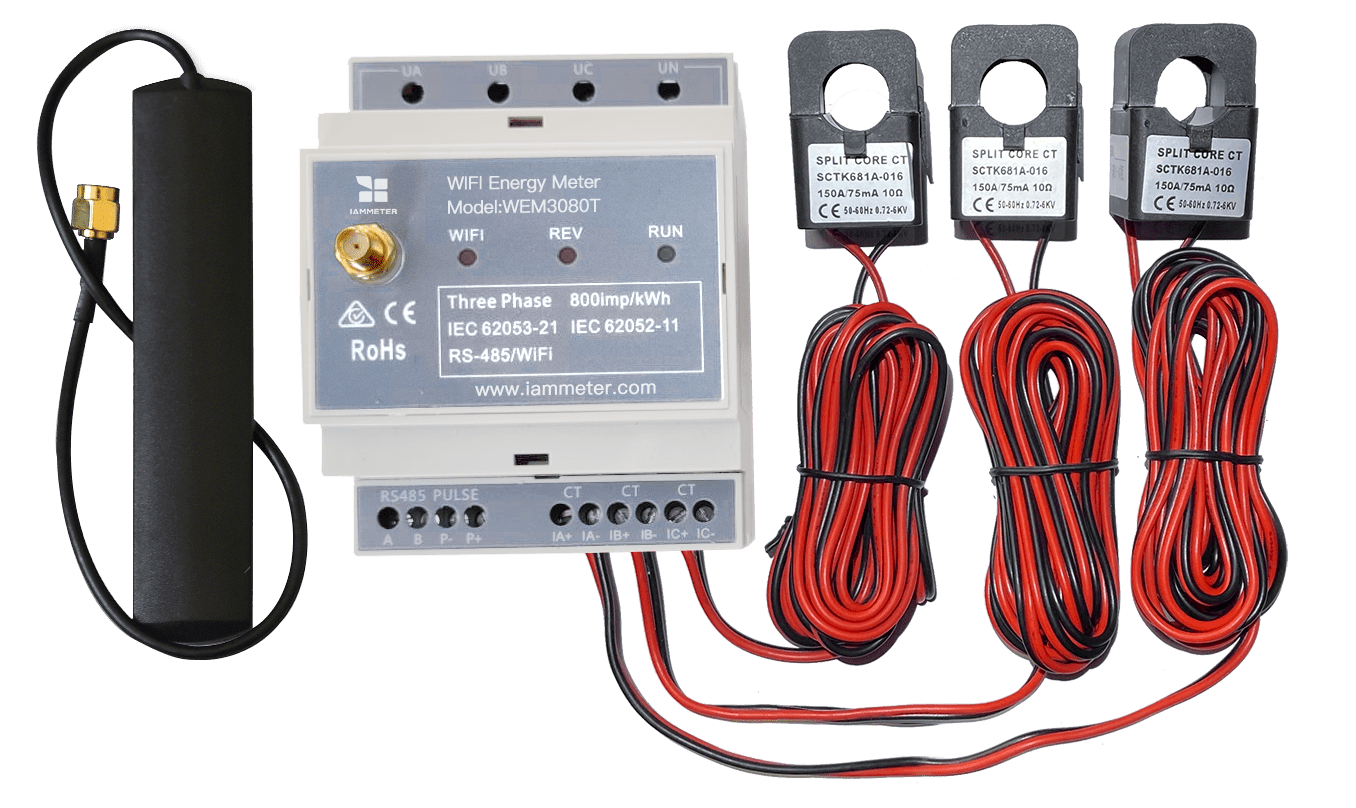
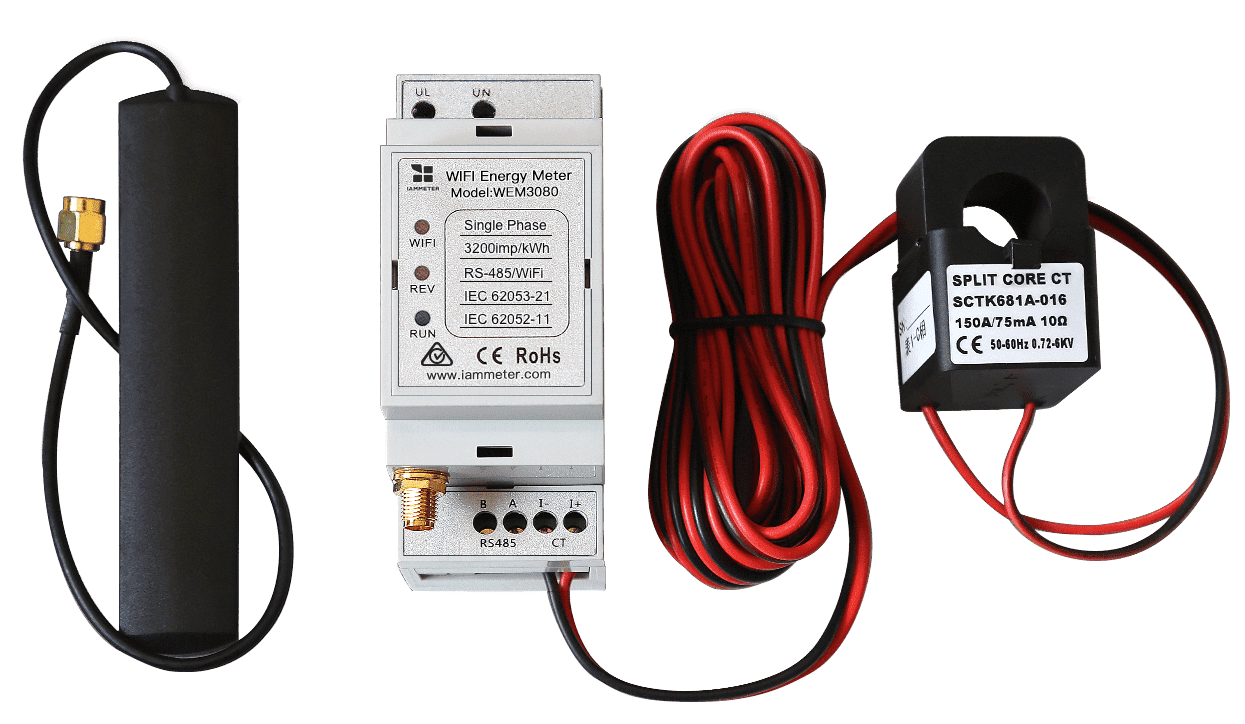
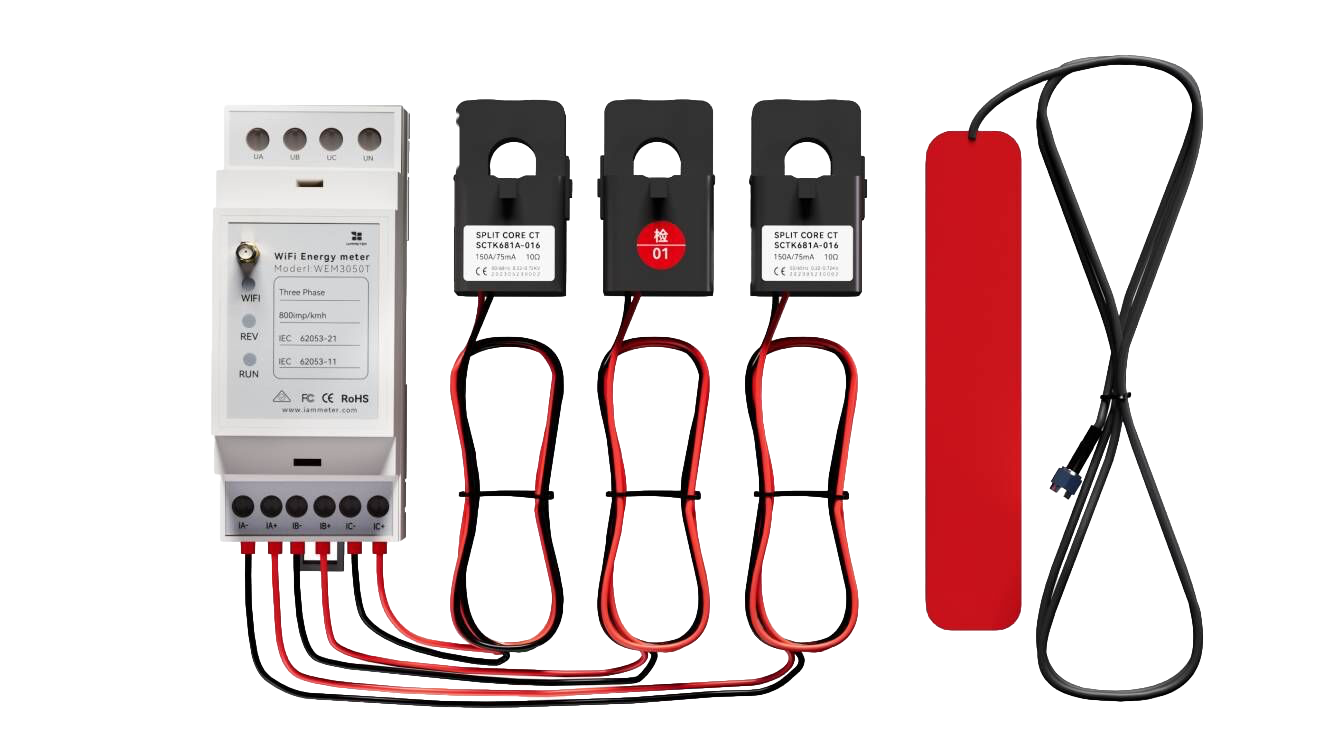
Estimate the profit of the energy storage system based on your actual grid consumption.
How to estimate the possible profit of the energy-storage before you install it
The topic is from this discussion home battery simulation. One customer wants to estimate the battery capacity he needs before introducing the energy storage system.
After the discussion ,we've discovered that IAMMETER-cloud can help customers assess battery capacity using their own real data.
Preface: Why Consider Implementing an Energy Storage System
As the inverter installation is more popular, the feed in price is far less than the electricity price now. You may only earn 0.05 AUD when feeding 1 kwh to the grid but have to pay 0.3-0.4 AUD when consuming 1kwh from the grid. So the price difference make the energy storage system is meaningful.
Another approach is to manage the load effectively, such as activating high-energy-consuming appliances like water heaters when solar generation is at its peak. We previously discussed this strategy here. If attempts to control the load haven't fully utilized solar energy and there's significant surplus fed back into the grid at a low feed-in price, while facing high electricity costs during peak periods, implementing an energy storage system becomes a viable option.
When aiming to profit from an energy storage system, it's essential to first carefully consider the following questions:
- Whether the price (on-peak price vs. off-peak price, or feed-in price vs. electricity price) difference is sufficient ?
- What is the grid consumption during specific hours within a period (e.g., on-peak hours), and what are the associated electricity costs?
- How many kWh are exported to the grid on a daily, monthly, or other periodic basis?
- What portion of electricity consumption is most cost-effective to be covered by battery capacity?
What does IAMMETER-cloud offer
"Exported energy" and "Grid consumption"
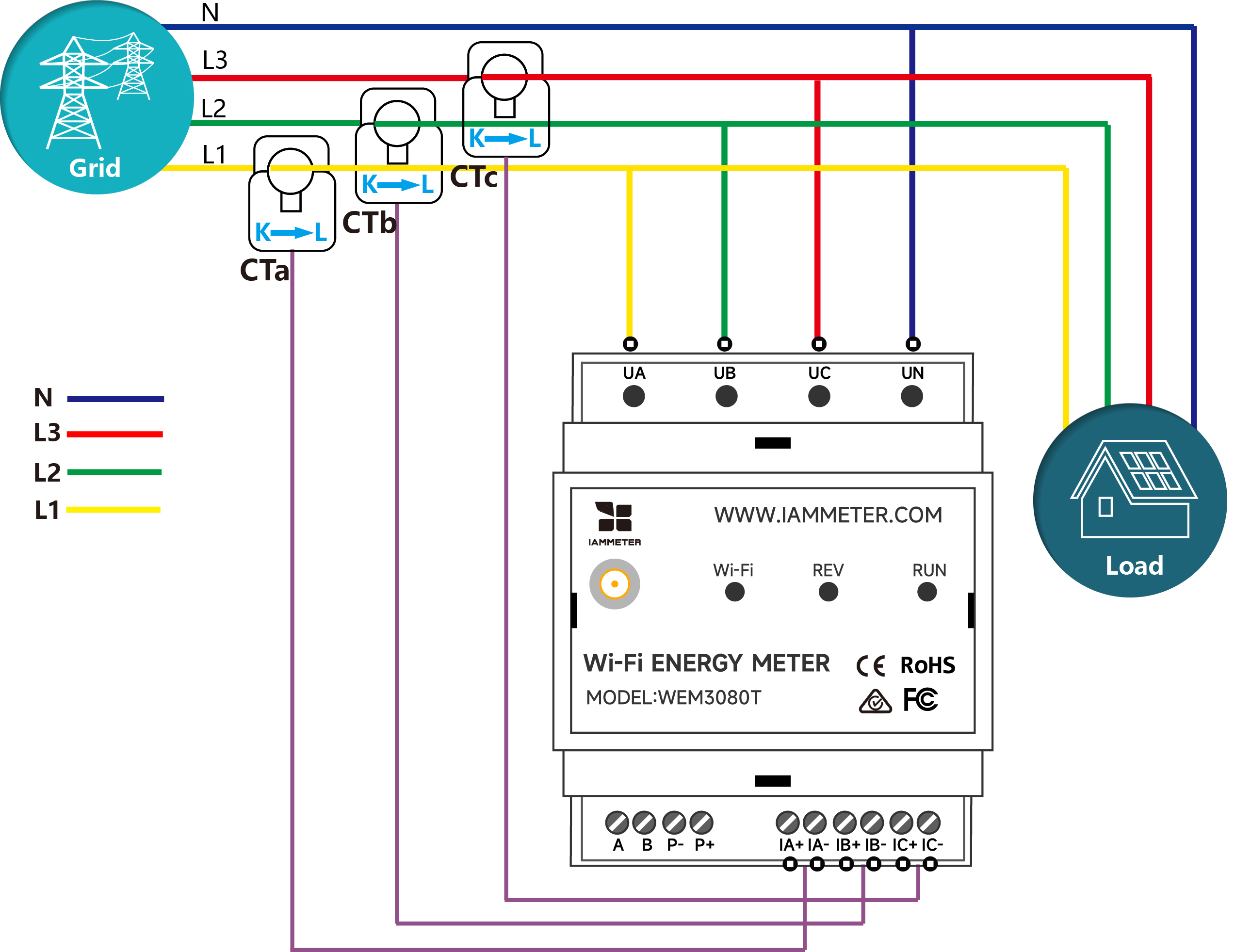
When an IAMMETER energy meter is installed on the grid side, it provides two sets of kWh data:
Exported energy: the kilowatt-hours (kWh) generated by the solar inverter and exported to the grid.
Grid consumption: the kilowatt-hours (kWh) consumed from the grid.
The estimation of battery capacity would be based on these two parameters.
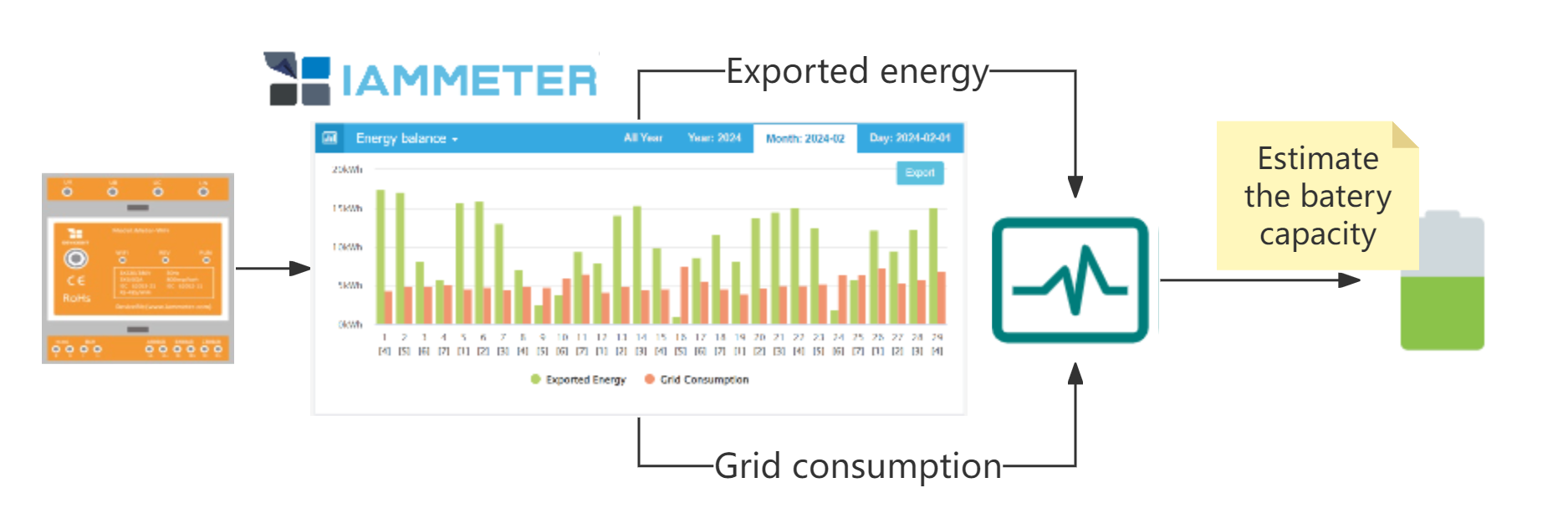
Estimation approach
The reason for introducing an energy storage system is because the energy transferred through the battery can yield profits.
The profit can be represented by a formula: $$ Profit = Price Difference * BatteryCycle(Kwh) . $$ Price Difference :the cost of consuming 1 kWh from the grid minus the cost of charging the battery with 1 kWh
In this tutorial, we focus on these four factors.
- On-Peak Grid Consumption (kWh) and Solar Exported kWh (if available).
- The electricity price of the on-peak period.
- The cost of charging the battery.
The first factor can be analyzed through the charts or reports in IAMMETER-cloud. With this data, combined with the price difference between on-peak electricity consumption and feed-in (if there's no photovoltaic, users can also consider charging during off-peak hours), users can roughly assess the potential profits of the energy storage system.
Analyzing Grid Consumption during the on-peak period
All data presented in this blog is sourced from the IAMMETER demo account.
You can also log in IAMMETER`s demo account by this link, please visit it by a PC browser .Otherwise it will be the APP effect if you visit it by a mobile browser.
Log in IAMMETER`s demo account by PC browser
"Energy Balance" Chart
If you wish to cover all periods (0:00-24:00) of your electricity consumption with the battery, the "energy balance" chart can help you quickly analyze the required battery capacity.
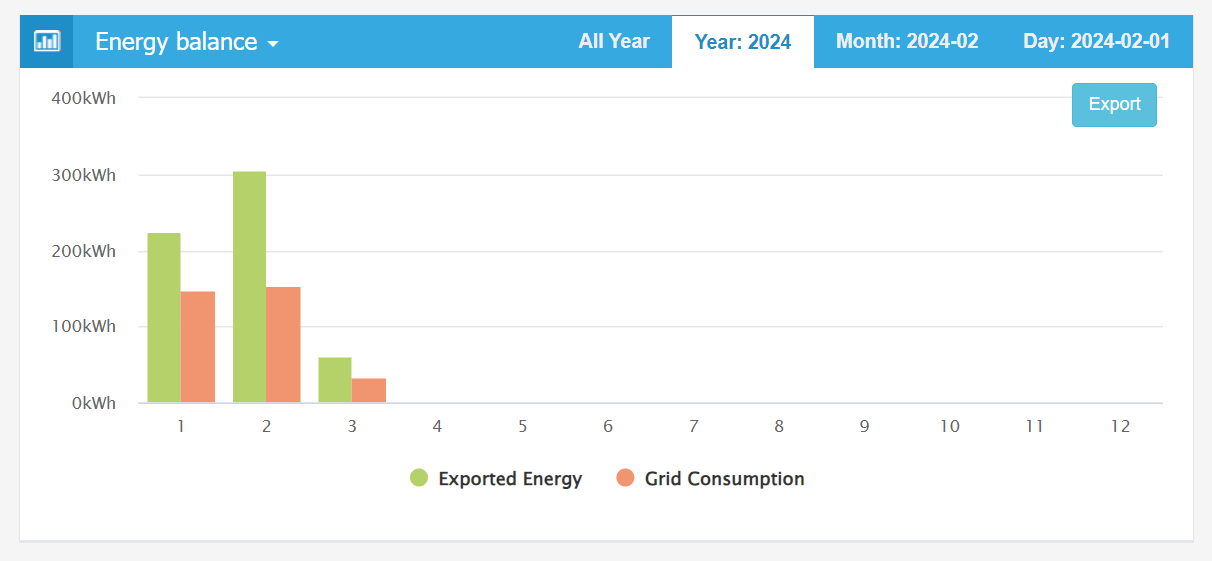
In the "Overview" dashboard, you can observe the daily, monthly, or yearly feed-in kWh values from the graph displayed below.
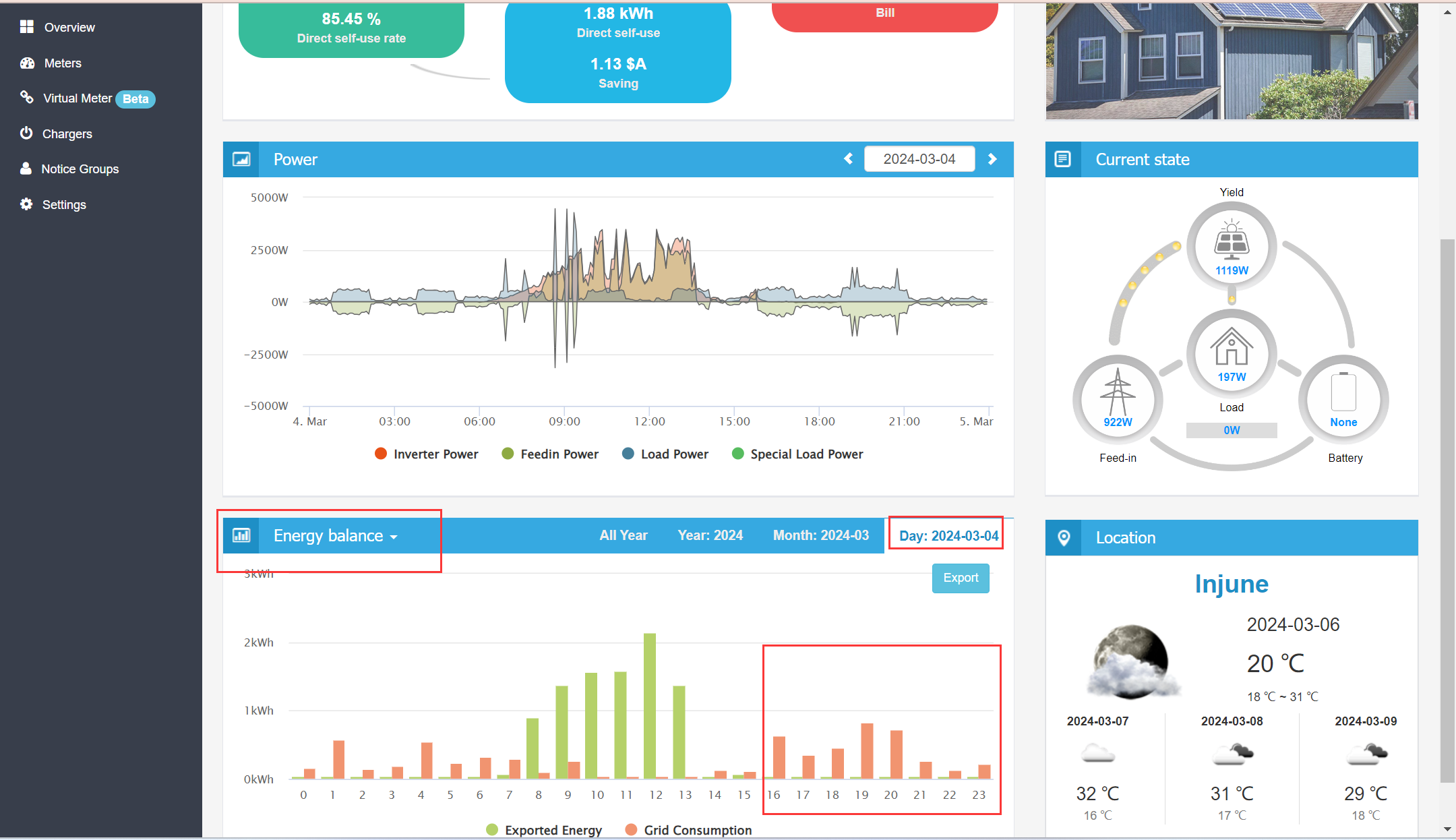
Energy-balance - Hourly
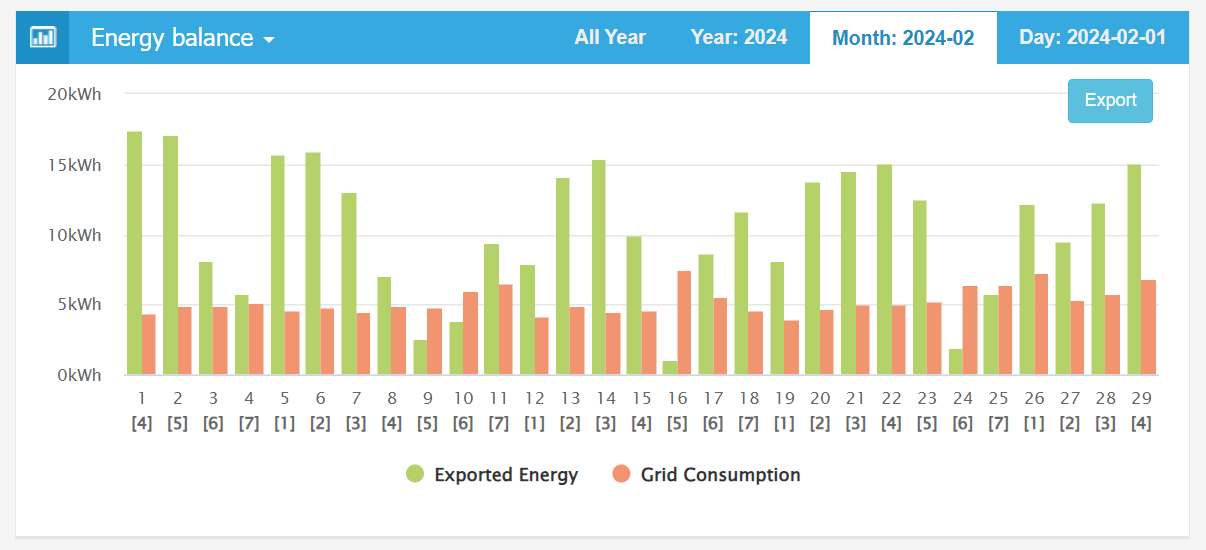
| Energy-balance - Daily (February) | Energy-balance - Monthly (2024) |
|---|---|
 |
 |
If you want to use a battery to cover your electricity consumption throughout the day, you can choose the battery capacity based on the daily grid consumption kWh (This assumes that there is sufficient solar output to fully charge the battery).
For example, from the data provided for February, it can be seen that the daily grid consumption is approximately 5 kWh. Given that the exported energy is far exceeds 5 kWh, you can choose a battery capacity of around 5 kWh (Of course, considering seasonal variations, data from different months may vary, so it's necessary to consider data from multiple months).
The "energy balance" chart is only suitable for analyzing grid consumption throughout the entire day. If you want to analyze grid consumption during a specific time period (such as on-peak hours), you can use the report introduced in the next section.
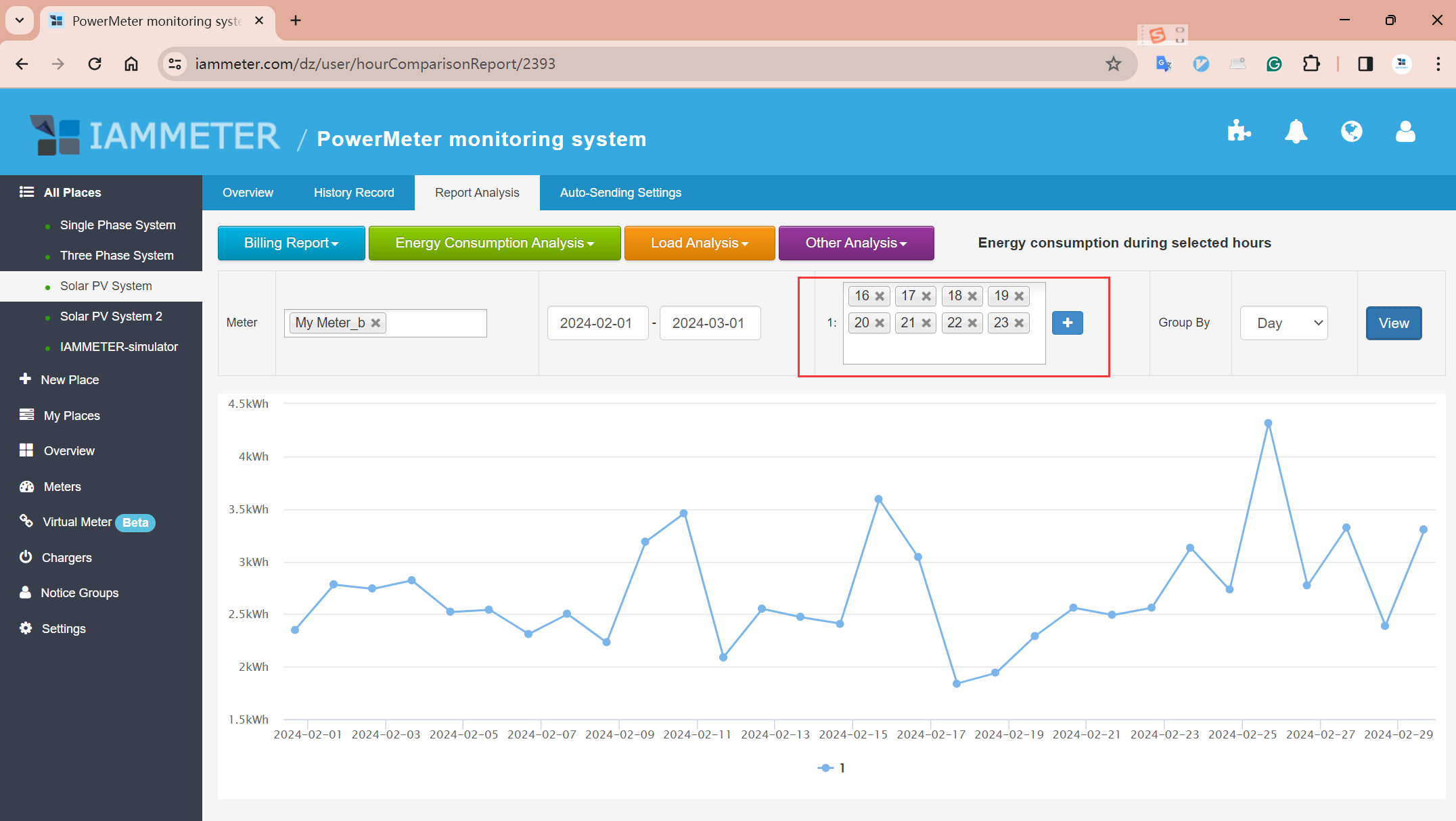
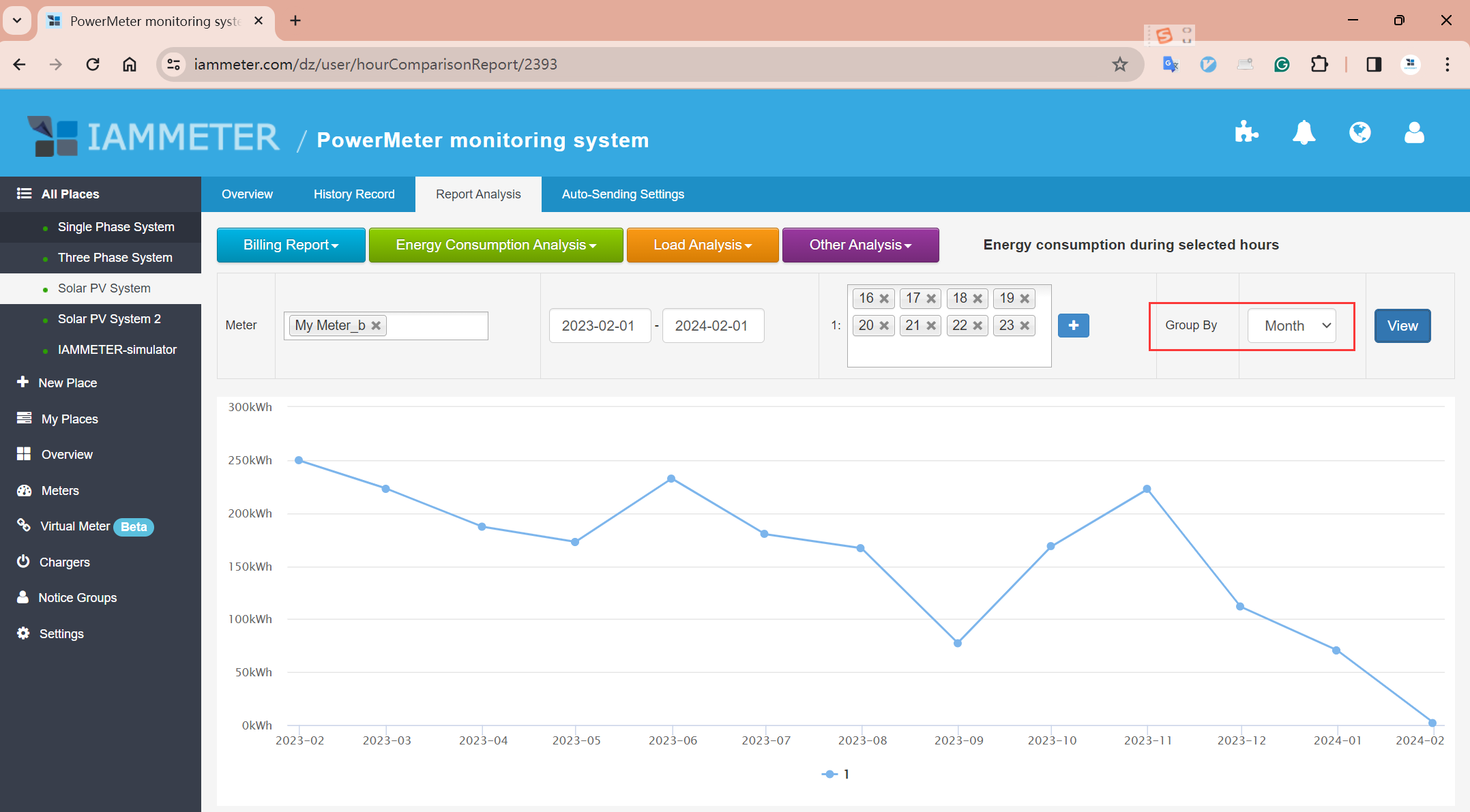
Report: Energy consumption during selected hour
If you specifically want the battery to cover grid consumption during on-peak hours(Ex:16:00-24:00), the energy balance chart may not be sufficient. In this case, you'll need to use this Analysis of grid consumption during selected hour
New Report(Coming soon): Estimating the Benefits of Battery Implementation
Although the previous chart and report can assist users in completing a simple analysis of battery capacity, the analysis results may not be direct enough.
Therefore, we plan to provide a new report.
Customers only need to input a battery capacity and the associated investment costs, and IAMMETER-cloud will simulate a battery in the system and generate a new bill based on historical electricity consumption data.
Customers can also input different battery capacities to experience the impact of batteries of different capacities on their bills.
Reference
Monitor the solar PV in IAMMETER-1
What capabilities does IAMMETER offer?
Which type of electrical meter best fits your needs?
How to estimate the possible profit of the energy-storage before you install it
The topic is from this discussion home battery simulation. One customer wants to estimate the battery capacity he needs before introducing the energy storage system.
After the discussion ,we've discovered that IAMMETER-cloud can help customers assess battery capacity using their own real data.
Preface: Why Consider Implementing an Energy Storage System
As the inverter installation is more popular, the feed in price is far less than the electricity price now. You may only earn 0.05 AUD when feeding 1 kwh to the grid but have to pay 0.3-0.4 AUD when consuming 1kwh from the grid. So the price difference make the energy storage system is meaningful.
Another approach is to manage the load effectively, such as activating high-energy-consuming appliances like water heaters when solar generation is at its peak. We previously discussed this strategy here. If attempts to control the load haven't fully utilized solar energy and there's significant surplus fed back into the grid at a low feed-in price, while facing high electricity costs during peak periods, implementing an energy storage system becomes a viable option.
When aiming to profit from an energy storage system, it's essential to first carefully consider the following questions:
- Whether the price (on-peak price vs. off-peak price, or feed-in price vs. electricity price) difference is sufficient ?
- What is the grid consumption during specific hours within a period (e.g., on-peak hours), and what are the associated electricity costs?
- How many kWh are exported to the grid on a daily, monthly, or other periodic basis?
- What portion of electricity consumption is most cost-effective to be covered by battery capacity?
What does IAMMETER-cloud offer
"Exported energy" and "Grid consumption"

When an IAMMETER energy meter is installed on the grid side, it provides two sets of kWh data:
Exported energy: the kilowatt-hours (kWh) generated by the solar inverter and exported to the grid.
Grid consumption: the kilowatt-hours (kWh) consumed from the grid.
The estimation of battery capacity would be based on these two parameters.

Estimation approach
The reason for introducing an energy storage system is because the energy transferred through the battery can yield profits.
The profit can be represented by a formula: $$ Profit = Price Difference * BatteryCycle(Kwh) . $$ Price Difference :the cost of consuming 1 kWh from the grid minus the cost of charging the battery with 1 kWh
In this tutorial, we focus on these four factors.
- On-Peak Grid Consumption (kWh) and Solar Exported kWh (if available).
- The electricity price of the on-peak period.
- The cost of charging the battery.
The first factor can be analyzed through the charts or reports in IAMMETER-cloud. With this data, combined with the price difference between on-peak electricity consumption and feed-in (if there's no photovoltaic, users can also consider charging during off-peak hours), users can roughly assess the potential profits of the energy storage system.
Analyzing Grid Consumption during the on-peak period
All data presented in this blog is sourced from the IAMMETER demo account.
You can also log in IAMMETER`s demo account by this link, please visit it by a PC browser .Otherwise it will be the APP effect if you visit it by a mobile browser.
Log in IAMMETER`s demo account by PC browser
"Energy Balance" Chart
If you wish to cover all periods (0:00-24:00) of your electricity consumption with the battery, the "energy balance" chart can help you quickly analyze the required battery capacity.
In the "Overview" dashboard, you can observe the daily, monthly, or yearly feed-in kWh values from the graph displayed below.
Energy-balance - Hourly

| Energy-balance - Daily (February) | Energy-balance - Monthly (2024) |
|---|---|
 |
 |
If you want to use a battery to cover your electricity consumption throughout the day, you can choose the battery capacity based on the daily grid consumption kWh (This assumes that there is sufficient solar output to fully charge the battery).
For example, from the data provided for February, it can be seen that the daily grid consumption is approximately 5 kWh. Given that the exported energy is far exceeds 5 kWh, you can choose a battery capacity of around 5 kWh (Of course, considering seasonal variations, data from different months may vary, so it's necessary to consider data from multiple months).
The "energy balance" chart is only suitable for analyzing grid consumption throughout the entire day. If you want to analyze grid consumption during a specific time period (such as on-peak hours), you can use the report introduced in the next section.
Report: Energy consumption during selected hour
If you specifically want the battery to cover grid consumption during on-peak hours(Ex:16:00-24:00), the energy balance chart may not be sufficient. In this case, you'll need to use this Analysis of grid consumption during selected hour


New Report(Coming soon): Estimating the Benefits of Battery Implementation
Although the previous chart and report can assist users in completing a simple analysis of battery capacity, the analysis results may not be direct enough.
Therefore, we plan to provide a new report.
Customers only need to input a battery capacity and the associated investment costs, and IAMMETER-cloud will simulate a battery in the system and generate a new bill based on historical electricity consumption data.
Customers can also input different battery capacities to experience the impact of batteries of different capacities on their bills.
Updated on April 12th, 2024:
The latest report is now available. You can access it here: Report Predicts Benefits of Battery Storage"
Reference
Monitor the solar PV in IAMMETER-1